Understanding Osteoporosis: Different Stages of Osteoporosis

Compassionate Osteoporosis: Different Stages of Osteoporosis
Your bones naturally weaken as you age, making them more prone to fractures and breaks. But did you know there are four distinct stages of osteoporosis, affecting millions worldwide? Understanding these stages is crucial in preventing and managing bone loss. In this article by The Valencia Home by MD Senior Living, we’ll guide you through the different stages of osteoporosis, from the early, symptom-free phases to the more advanced stages that can cause pain, deformities, and increased risk of fractures. By grasping the progression of osteoporosis, you’ll be better equipped to take control of your bone health and make informed decisions about prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
How Do You Determine the Severity of Osteoporosis?
The diagnosis of osteoporosis involves determining the severity of bone loss, which is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will use various methods to assess the severity of your osteoporosis.
Bone Density Tests
Bone density tests, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans, can detect changes in bone density. These tests measure the mineral density in each square centimeter of bone, providing a T-score indicating the bone loss level.
FRAX Assessment
Determine your fracture risk using the FRAX assessment, a calculation tool that considers your bone density, age, sex, weight, and other risk factors. This assessment helps your healthcare provider predict your 10-year probability of experiencing a major osteoporotic fracture.
A FRAX assessment is instrumental in identifying individuals who may not have osteoporosis according to their bone density scores but are still at high risk of fracture due to other factors. By combining the results of your bone density test and FRAX assessment, your healthcare provider can develop a personalized treatment plan to reduce your risk of fractures and manage your osteoporosis effectively.
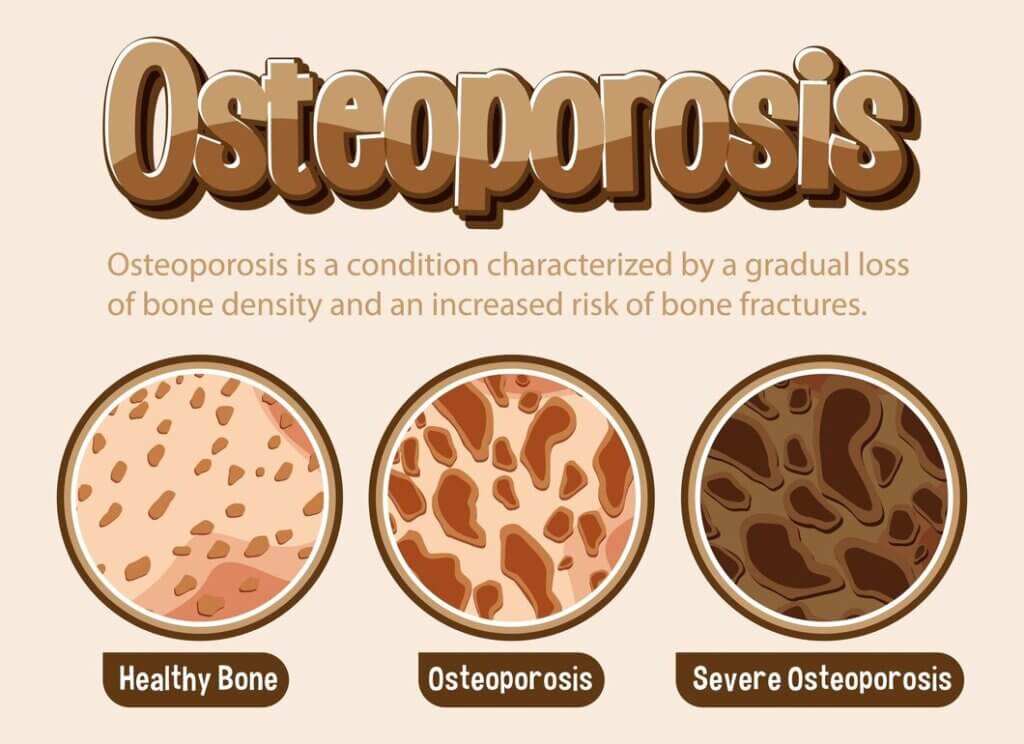
Stages of Osteoporosis
Little do you know, osteoporosis is a gradual process that can be categorized into four distinct stages. Understanding these stages is crucial in diagnosing and managing the condition effectively.
Definition
The stages of osteoporosis refer to the progressive decline in bone density and strength, which leads to increased fragility and susceptibility to fractures. Distinct symptoms, bone density scores, and treatment options characterize each stage.
Characteristics
Stages of osteoporosis are marked by varying degrees of bone loss, ranging from mild to severe. As you progress from one stage to the next, your bone density scores decrease and your risk of fractures and deformities increases.
Each stage is defined based on the T-score, which measures bone density. A T-score of -1 to -2.5 indicates osteopenia, while a score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis.
Average Bone Density (Stage 1)
Definition: In this stage, your bone density is average, with a T-score ranging from +1 to -1. You may not experience any symptoms, and your bones are still strong and healthy.
Characteristics: At this stage, your bones are growing and breaking down at an average rate. You may not require any treatment, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is necessary.
Osteopenia (Stage 2)
Definition: In this stage, your bone density is lower than usual, with a T-score between -1 and -2.5. You may not experience any symptoms, but your bones are weakening.
Characteristics: Your bone loss is accelerating at this stage, and you may risk developing osteoporosis. Your healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle changes, such as increasing calcium and vitamin D intake and exercising regularly.
Osteoporosis (Stage 3)
Definition: In this stage, your bone density is significantly low, with a T-score of -2.5 or lower. You may experience symptoms such as back pain, stooped posture, and increased risk of fractures.
Characteristics: At this stage, your bones are fragile and prone to fractures. Your healthcare provider may recommend medications like bisphosphonates to slow down bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
Definition: In this stage, your bone density is severely low, with a T-score below -2.5. You may experience severe symptoms, such as chronic pain, deformities, and frequent fractures.
Characteristics: Your bones are extremely fragile at this stage, and you may require ongoing medical attention. Your healthcare provider may recommend a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and physical therapy to manage your symptoms.
Risks and Complications
Risks of osteoporosis include fractures, deformities, and chronic pain. If left untreated, osteoporosis can significantly impact your quality of life, making everyday activities challenging and increasing your risk of falls and injuries.
Osteoporosis can also affect your mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and social isolation. Working with your healthcare provider to manage your symptoms and prevent complications is necessary.
Impact on Daily Life
One of the most significant impacts of osteoporosis is on your daily life. As your bones weaken, you may experience chronic pain, limited mobility, and decreased independence.
Life with osteoporosis can be challenging, but with the proper treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage your symptoms and maintain your quality of life. Working with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and goals is necessary.
If you’re concerned about osteoporosis or have been diagnosed, contact The Valencia Home by MD Senior Living at 480-605-4002 to learn more about our services and support. Understanding the stages of osteoporosis is crucial in managing the condition and maintaining your quality of life.
What Are the Risk Factors for Osteoporosis?
Your risk of developing osteoporosis depends on various factors, including age, gender, family history, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions. Understanding these risk factors can help you take preventive measures to reduce your chances of developing osteoporosis.
- Age and Gender
- Family History and Genetics
- Lifestyle Choices
- Medical Conditions and Medications
Recognizing these risk factors can help you proactively prevent or manage osteoporosis.
Age and Gender
When one reaches a certain age, bones naturally start to lose density. Due to the decline in estrogen levels, women, especially those who have reached menopause, are more likely to develop osteoporosis. Although it’s less common in men, it can also occur in women.
Family History and Genetics
Any family history of osteoporosis or fractures can increase your risk of developing the condition. Additionally, certain genetic disorders, such as osteogenesis imperfecta, can affect bone density and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Plus, if you have a family history of osteoporosis, it’s vital to talk to your healthcare provider about your risk factors and take preventive measures to reduce your chances of developing the condition.
Lifestyle Choices
For healthy bone density, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is vital. A sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can all contribute to an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Genetics plays a significant role in osteoporosis, but lifestyle choices can also affect bone health. By making healthy choices, you can reduce your risk of developing osteoporosis.

Medical Conditions and Medications
Any medical condition that affects hormone levels, such as hyperthyroidism or Cushing’s syndrome, can increase your risk of osteoporosis. Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and anticonvulsants, can also contribute to bone loss.
Lifestyle modifications and medication management can help reduce the risk of osteoporosis associated with medical conditions and medications.
How Can I Stop Bone Loss?
Once again, the good news is that you can take steps to slow down or even stop bone loss. While you can’t completely prevent osteoporosis, mainly if it’s caused by underlying diseases or aging, you can make lifestyle changes and take supplements to support your bone health.
Diet and nutrition play a significant role in maintaining strong bones. For a healthy bone diet, focus on consuming foods rich in calcium and vitamin D, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fatty fish.
Diet and Nutrition
Aim to consume 1,000-1,200 milligrams of calcium and 400-800 international units of vitamin D daily for optimal bone health. You can get these nutrients through a balanced diet or supplements, but always consult your healthcare provider before adding new supplements to your routine.
Smoking Cessation
The negative impact of smoking on bone health cannot be overstated. Smoking cessation is crucial to preventing further bone loss and reducing the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures.
Loss of bone density is a significant concern for smokers, as nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco products can interfere with bone cell function and reduce bone mass. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your overall health, including your bone health.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Smoking is not the only lifestyle habit that can harm your bones; excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to bone loss. Limiting your alcohol intake can help reduce the risk of osteoporosis and related fractures.
Understanding the impact of excessive alcohol consumption on bone health is imperative. Excessive drinking can lead to a decrease in bone density, making your bones more susceptible to fractures and osteoporosis.
Calcium and Vitamin D
Consumption of adequate calcium and vitamin D is crucial for maintaining strong bones. These nutrients work together to promote bone growth and density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and related fractures.
A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help support bone health. Foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fatty fish are excellent sources of these imperative nutrients.
Other Nutrients and Vitamins
Bone health is not just about calcium and vitamin D; other nutrients and vitamins, such as vitamin K, magnesium, and potassium, also play a significant role in maintaining strong bones.
Nutrients like vitamin K, magnesium, and potassium can help regulate bone metabolism, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and related fractures. Incorporating foods rich in these nutrients into your diet can help support overall bone health.
Weight-Bearing Exercises
Smoking cessation and a healthy diet are not the only ways to support bone health; regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing, can also help maintain strong bones.
Regular weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, or weightlifting, can improve your bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and related fractures.
Resistance Training
Resistance training, which involves using weights or resistance bands to strengthen your muscles, can also help improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Weight-bearing exercises like squats and lunges can help strengthen your bones. At the same time, resistance training can improve muscle mass and bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures.
Bisphosphonates
Weight-bearing exercises and a healthy diet are not the only ways to support bone health; medications like bisphosphonates can also help slow down or stop bone loss.
Bisphosphonates are another option for treating osteoporosis. They can help reduce the risk of fractures by slowing down bone resorption and increasing bone density.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
For women, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be an option to help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
For women experiencing menopause, HRT can help regulate hormone levels, reducing the risk of bone loss and osteoporosis. However, discussing the risks and benefits of HRT with your healthcare provider before starting treatment is imperative.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes and supplements into your daily routine, you can take control of your bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Remember to consult your healthcare provider before significantly changing your diet or exercise routine.
Managing Osteoporosis
Not everyone with osteoporosis will experience severe symptoms, but with the right management plan, you can reduce your risk of fractures and improve your overall quality of life.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
Effective management plans start with a strong partnership between you and your healthcare provider. They will work with you to develop a personalized plan that considers your unique needs, medical history, and lifestyle.
Creating a Personalized Plan
For optimal management, it is essential to create a plan that addresses your specific needs and risk factors. This plan may involve a combination of lifestyle changes, supplements, and medications.
Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular bone density tests to monitor your progress and adjust your plan. By working together, you can develop a comprehensive plan that helps you manage your osteoporosis and maintain your independence.
Taking proactive steps to manage your osteoporosis can reduce your risk of fractures and improve your overall quality of life. At The Valencia Home by MD Senior Living in Scottsdale, AZ, our team is dedicated to providing personalized care and support to help you thrive. Contact us today at 480-605-4002 to learn more about our services and how we can help you manage your osteoporosis.
Preventing Fractures
For individuals living with osteoporosis, preventing fractures is a crucial aspect of managing the condition. Fractures can significantly impact daily life, causing pain, disability, and life expectancy. Fortunately, several strategies can help prevent fractures and reduce the risk of osteoporosis-related injuries.
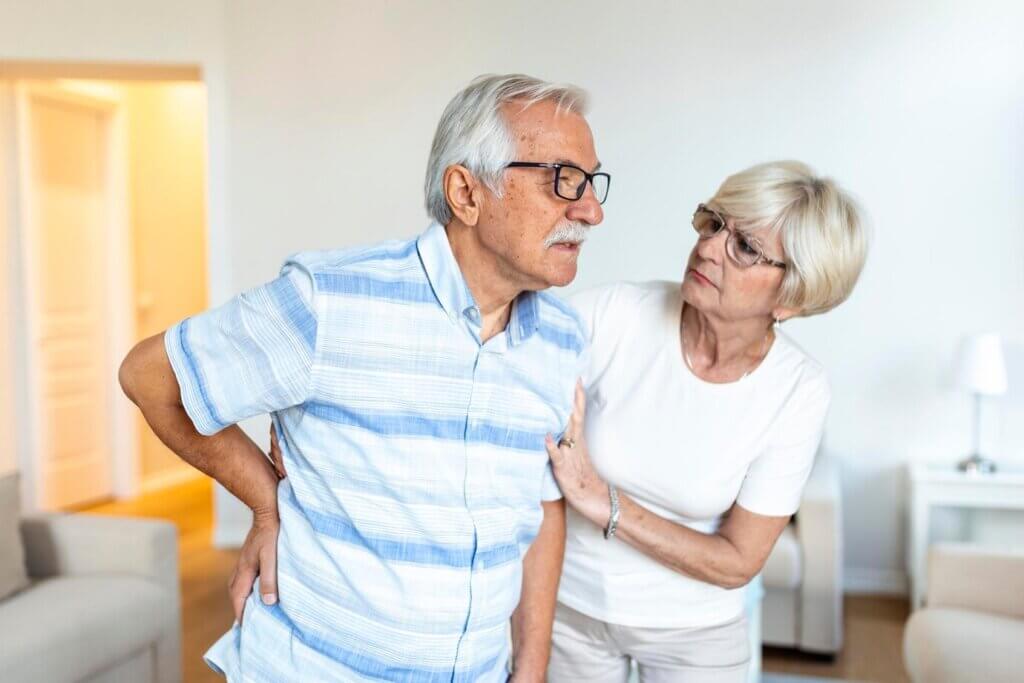

Fall Prevention Strategies
Falling can be a significant risk factor for fractures, especially for individuals with osteoporosis. Falling hazards can be found in many places, including the home, outdoors, and public spaces. To reduce the risk of falls, it’s essential to identify and remove tripping hazards, improve lighting, and install handrails or grab bars in critical areas. Exercising regularly to improve balance and strength can also help prevent falls.
Safe Movement and Exercise
Fractures can often be prevented by engaging in safe movement and exercise practices. This includes avoiding activities that involve bending, twisting, or heavy lifting, which can strain the bones excessively. Instead, focus on exercises that promote flexibility, balance, and strength, such as yoga, Pilates, or swimming.
Strategies for safe movement and exercise include
- incorporating exercises that target the core muscles,
- improving posture, and
- using proper body mechanics when lifting or bending.
It’s also essential to consult with a healthcare provider or fitness professional to develop a personalized exercise plan that takes into account individual needs and abilities.
By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals with osteoporosis can reduce their risk of fractures and maintain independence and mobility. At The Valencia Home by MD Senior Living in Scottsdale, AZ, our team is dedicated to providing supportive care and resources to help individuals manage osteoporosis and improve their overall quality of life. Contact us at 480-605-4002 to learn more about our services and how we can help.
Conclusion
Summing up, understanding the different stages of osteoporosis is crucial for preventing and managing this debilitating condition. By recognizing the four stages of osteoporosis, from the initial bone loss to the severe symptoms of stage 4, you can take proactive steps to maintain your bone health. Remember, while osteoporosis can be a challenging condition to live with, making lifestyle changes, taking supplements, and seeking medical treatment can significantly slow its progression. At The Valencia Home by MD Senior Living, we care about your health and well-being. Don’t hesitate to contact us at 480-605-4002. Take control of your bone health today!




Leave a Comment